
Ensuring that public venues are accessible is both a legal requirement and a mark of inclusive design. Meeting public venue accessibility requirements under UK law ensures that all visitors, including those with disabilities, can access facilities safely, comfortably and independently. From planning entrances and seating arrangements to providing ramps and wayfinding solutions, effective accessibility planning supports compliance while creating welcoming spaces for everyone.
This guide explains key considerations for wheelchair access in public buildings, best practices in accessibility planning for public spaces, and how to meet disabled access compliance UK standards effectively.
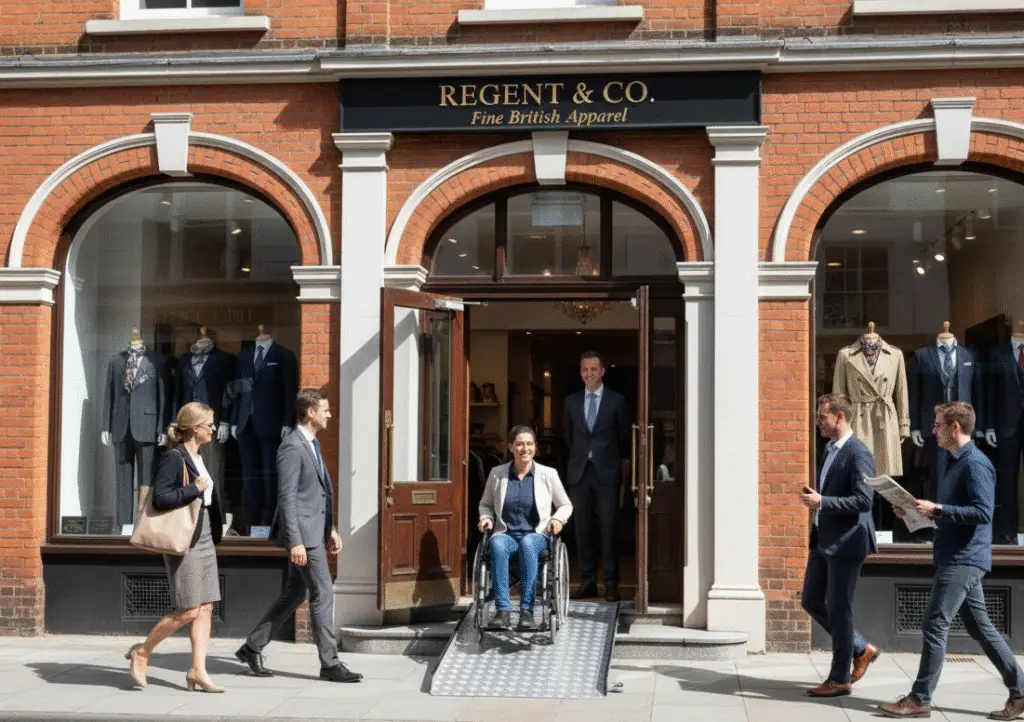

Public venues are expected to comply with the Equality Act 2010 and relevant UK building regulations, which set out responsibilities for providing reasonable adjustments to remove barriers. Compliance includes:
Meeting these requirements ensures your venue is safe, inclusive and legally compliant, while enhancing the experience for all visitors.
A critical element of accessibility planning is providing wheelchair access for public buildings. When designing access:
Effective planning balances practical usability with legal compliance, helping venues avoid costly retrofits later.
Effective accessibility planning for public spaces goes beyond installing ramps and widening doors. It also involves providing clear signage and wayfinding for visually impaired visitors, ensuring accessible restroom facilities, training staff to assist people with mobility limitations, and planning for safe evacuation and emergency procedures.
By incorporating these measures into the design and management of public venues, operators can meet public venue accessibility requirements, support wheelchair access for public buildings, and maintain disabled access compliance UK, creating inclusive and safe experiences for all visitors.
The UK’s disabled access compliance regulations guide how venues should provide equal access. Key measures include:
Compliance is not just a legal obligation, it demonstrates a commitment to inclusion and enhances reputation with visitors and stakeholders.
Different public venues have varying needs, and both temporary event ramps and permanent/modular ramps may be appropriate:
Permanent ramps are the ideal solution for main entrances, high-traffic areas and venues that require long-term accessibility compliance. These ramps are typically fixed in place and can be customised to fit complex layouts, varying gradients and landing requirements. Modular designs allow flexibility while maintaining safety standards, ensuring smooth wheelchair access for public buildings.
Temporary ramps are best suited for short-term events, secondary entrances or locations where permanent installation is not feasible. Despite being portable, they must be stable, safe and easy for staff to deploy quickly. These ramps provide step-free access for wheelchair users and other mobility devices, ensuring that temporary setups still comply with public venue accessibility requirements and support wheelchair access for public buildings.
Creating a fully accessible public venue requires careful planning, ongoing evaluation, and attention to both legal and practical requirements. By prioritising accessibility from the start, venues can provide safe, welcoming and inclusive environments for all visitors while maintaining the UK’s public venue accessibility requirements and disabled access compliance.
Key Tips for Accessibility Planning:
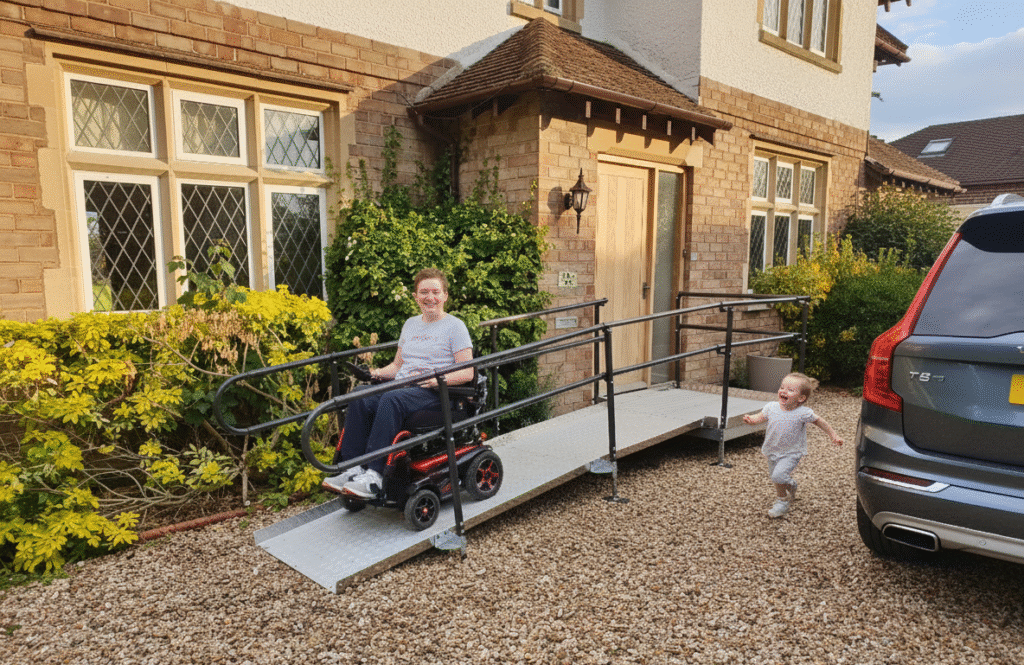
Planning for accessibility in public venues is about more than meeting legal obligations — it’s about creating safe, inclusive and welcoming spaces for all visitors. Understanding public venue accessibility requirements is the first step, but implementing the right solutions — such as permanent or temporary ramps — ensures practical, compliant and reliable wheelchair access for public buildings.
By taking a proactive approach, consulting experts and integrating accessibility into both design and operations, venue operators can maintain the disabled access compliance required in the UK, improve visitor experience, and avoid costly retrofits or legal risks. Thoughtful accessibility planning demonstrates a genuine commitment to inclusion while future-proofing your venue for evolving standards and expectations.
Public venues must ensure that all visitors, including those with disabilities, can access facilities safely and independently. This includes providing step-free entrances, wide circulation paths, accessible restrooms and safe emergency evacuation routes.
Ensuring wheelchair access for public buildings involves installing permanent or temporary ramps, designing level landings, adding handrails where needed, and keeping pathways clear of obstacles. Attention to gradients, width and surface materials is essential for safety and usability.
Temporary ramps can meet accessibility standards when permanent installations are not practical. They are ideal for events, short-term access needs or secondary entrances. However, they must be stable, easy to deploy and suitable for all users. Properly planned temporary ramps ensure that venues meet public venue accessibility requirements without compromising safety or accessibility.
Accessibility planning for public spaces ensures that all areas of a venue, including entrances, seating, restrooms, signage and emergency routes, are safe, functional and inclusive. Proactive planning helps venues meet legal obligations, avoids costly retrofits, and provides a positive experience for all visitors, including those with mobility limitations.
If steps or level changes prevent independent access, venues must provide step-free solutions. This can include permanent, modular or temporary ramps depending on the layout, visitor needs and frequency of use. Providing ramps ensures compliance with public venue accessibility requirements and supports safe, inclusive access for everyone.